Upload Image Html and Save in Folder Using Javascript and Vb.net
How to Upload Files in ASP.Cyberspace MVC
Uploading files from a client estimator to the remote server is quite a common chore for many websites and applications. It's widely used in social nets, forums, online auctions, etc.
There are a variety of upload components in ASP.Net MVC that serve to resolve one or another upload tasks, for example you may need to upload single or multiple files, work with files of modest or very large size, transfer entire folders or files merely, just upload images or preprsdfsdf s sd focess them beforehand. Thus, you lot need to find the upload tool that is not only fast and reliable, but too suits your requirements.
Hither we'll explore which upload approach is better to use when, but before that let's accept a look at ASP.NET MVC file upload in general.
File Upload Basics
During the file upload process, only two parts of the MVC model interact with each other – a view and a controller. Let's examine the file upload process step by pace:
- A user visits a web page with an uploader (represented by View) and chooses files to be uploaded.
- When the upload is started, the uploader packs the files into a POST request and sends this request to the server.
- ASP.NET caches all data in server memory or to disk depending on the uploaded file size.
- ASP.Net MVC defines the controller and advisable activity method that will handle the asking.
- The action method handles the request (for example, saves files on a hard disk, or updates a database, etc.) through the
Controller.Askingbelongings, which gets theHttpPostedFilesBaseobject for the current asking. - ASP.NET MVC sends an reply to the client through
Controller.Response.
You can configure file upload settings by specifying appropriate attributes in the web.config (or machine.config if you want to make server-wide changes). Let'southward see what attributes are used to limit the file upload:
-
maxRequestLength– the request size limit in kilobytes (the default value is 4096 KB). -
requestLengthDiskThreshold– the limit of data buffered in the server retentivity in kilobytes (the default value is lxxx KB). -
executionTimeout– the allowed execution time for the request before beingness automatically shut downwards by ASP.NET (the default value is 110 seconds).
All these attributes should be specified in the <httpRuntime> section.
Note: Avoid specifying "unlimited" (very large) values at that place. Specifying realistic limits, yous can ameliorate the operation of your server or reduce the risk of DoS attacks.
We've basically described how ASP.Internet MVC organizes file upload. However, if we look deeper into it, nosotros'll empathise that the file upload also depends on the View implementation: it can exist elementary <input blazon="file"> elements, HTML5, Wink, Java, or preexisting third-party uploader applications. Allow's start with the first ane – single file upload using the HTML control.
Single File Upload
This approach has quite limited functionality, but it'southward still the simplest fashion to upload a unmarried file at a fourth dimension and will work in any popular browser.
Firstly, we consider the view. Our view consists of an HTML form containing the button, which opens a select file dialog, and Submit, which sends the chosen file to the server in a POST request. The view code with razor syntax may look equally follows:
<h2>Bones File Upload</h2> @using (Html.BeginForm ("Index", "Home", FormMethod.Mail, new { enctype = "multipart/course-data" })) { <characterization for="file">Upload Prototype:</label> <input type="file" proper name="file" id="file"/><br><br> <input type="submit" value="Upload Image"/> <br><br> @ViewBag.Message } Let'south highlight the important parts:
- The
Html.BeginFormmethod creates an HTML form that includes the HTML file control, the submit button, and a message, which declares whether the file is saved successfully or not. - The form method is
POST, and the grade encoding type ismultipart/class-information. These parameters are required for uploading binary data to the server. - The
inputelement havingtype="file"displays the Choose File button and the field containing a selected file name. - The
proper nounof theinputelement identifies the uploaded file in theHttpPostedFilesBaseobject.
After a user submits the form, the View sends posted data to the Action method of the Controller that handles file upload. Draw attention on theHttpPost attribute before the activeness method - it says that the Activity should be triggered non only for regular GET requests, but besides Post requests. Otherwise information technology won't get the uploaded file.
Using this approach, you don't need to read the file from Request, because you tin access the POSTed file directly through the HttpPostedFilesBase object due to model bounden. The action model looks like this:
[HttpPost] public ActionResult Alphabetize(HttpPostedFileBase file) { if (file != null && file.ContentLength > 0) try { string path = Path.Combine(Server.MapPath("~/Images"), Path.GetFileName(file.FileName)); file.SaveAs(path); ViewBag.Message = "File uploaded successfully"; } catch (Exception ex) { ViewBag.Message = "Fault:" + ex.Message.ToString(); } else { ViewBag.Message = "Yous have not specified a file."; } return View(); } The activeness method receives the uploaded file, tries to salvage it to the Images binder, and shows a message indicating whether or non the file is saved successfully. Note, the input control name in the view has the aforementioned proper noun as the HttpPostedFilesBase object (it'south file in our instance).
After running this awarding you volition encounter the following class:
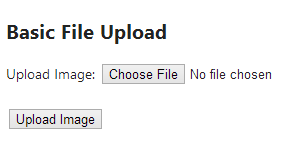
Once a user chooses a file and clicks the Upload Image push button, the post-obit class with the message (if the uploaded file is saved successfully) volition exist shown:
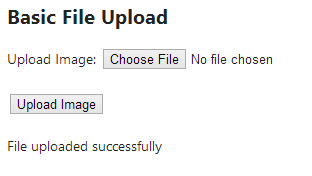
Keep security in mind!
Note: This elementary application allows you to transfer the user's files to y'all server, just information technology doesn't care about the security. The server may be compromised by a virus or other malicious data uploaded by someone. Thus, yous should add together some file upload restrictions to the controller. There are several security concerns, which allow yous to consider whether to accept an uploaded file or not. For example, y'all tin can verify the checksum of the uploaded file or control file blazon by checking the extension (but this tin be easily spoofed).
This arroyo is pretty good, if you lot upload a few pocket-sized files one by one, just it's rarely used due to the following disadvantages:
- Uploading a lot of files becomes a nightmare - a user has to click the Choose file button for each file.
- Uploading large files is not convenient - the folio freezes and doesn't display upload progress while the file upload is being processed.
- Afterwards submitting the grade all fields are cleared, thus if the form doesn't correspond to validation, a user has to fill all the fields again.
- Every browser displays the course in a different way:

Let's see how we can go across the disadvantages of this HTML control.
Multiple Files Upload
The awarding we discussed above can exist easily transformed to back up multiple file upload: but specify as many file inputs in the view every bit the number of files you lot desire to be uploaded simultaneously. Note, all inputs should have the aforementioned proper noun. This allows the ASP.NET MVC to have an array of uploaded files and iterate through them in the action method. However, in the example that a user needs to cull each file separately this is inconvenient, especially when uploading a large number of files.
Fortunately, at that place are many 3rd-party utilities supporting the multi-upload scenario and avoiding the shortcomings of the considered HTML control.
Whatsoever modern browser supports HTML5 and/or Flash, popular platforms which allow the creating of avant-garde file uploaders. Thus, there are a number of open up source HTML5/Flash-based uploaders bachelor with a large community of developers, for case:
- Uploadify is a jQuery plugin which allows you lot to build an upload interface like to Gmail attachments.
- Fine Uploader is a JavaScript plugin tool with multiple file pick, progress bar, auto and manual upload, paradigm preview, etc.
- Plupload is an upload tool based on several browser extensions, which includes some paradigm processing functionality.
These uploaders are very good at multiple file uploads and provide a simple interface, merely they cannot perform more complicated tasks, such every bit:
- Pre-process images before upload (resize, generate thumbnails of several sizes, add watermarks, extract EXIF, permit users crop images, etc.).
- Upload unabridged folders and keep the construction of the folders on the server.
- Upload hundreds of files.
- Upload files of hundreds of MB or fifty-fifty several GB.
- Automatically restore broken uploads.
- Speed up the upload process.
All these scenarios are ideal for Aurigma's Upload Suite. You can practise it with few lines of code.
See how to go started
Become a costless 30-day trial
Upload Suite includes premium uploaders based on various technologies (HTML5, Flash, Coffee, ActiveX) for any server engineering science – ASP.NET and PHP, classic ASP and JSP, Ruby-on-rails and node.js.
Source: https://www.aurigma.com/upload-suite/developers/aspnet-mvc/how-to-upload-files-in-aspnet-mvc